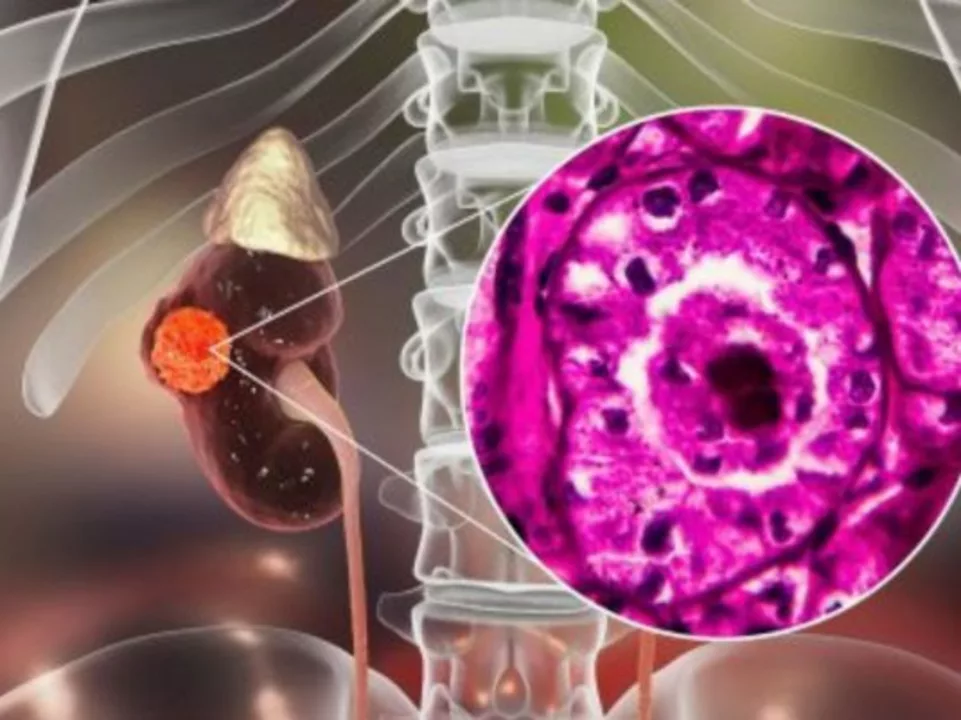
Recognizing the Symptoms of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
As someone who has experienced the effects of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) firsthand, I know how important it is to recognize the symptoms of this disease. In this section, we will discuss the most common signs that may indicate the presence of advanced RCC, such as fatigue, weight loss, and blood in the urine. It's crucial to keep in mind that these symptoms can also be caused by other, less serious conditions, so it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Moreover, other potential symptoms include persistent pain in the side or lower back, swelling in the legs or ankles, and a general feeling of malaise. Remember, early detection is key to improving the prognosis for advanced RCC, so don't hesitate to reach out to your doctor if you're experiencing any of these symptoms.
Understanding the Staging of Renal Cell Carcinoma
As a patient, one of the most confusing aspects of RCC is understanding its staging system. The purpose of this section is to help you grasp the different stages of this cancer, which will ultimately help you better comprehend your diagnosis and treatment options. The staging of RCC is based on the TNM system, which takes into account the size and extent of the primary tumor (T), whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes (N), and whether it has metastasized to other parts of the body (M).
There are four primary stages of RCC, with Stage I being the least advanced and Stage IV being the most advanced. As the cancer progresses, the treatment options and prognosis may change. It's essential to work closely with your healthcare team to ensure you receive the most appropriate care for your specific stage of RCC.
The Role of Surgery in Treating Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
When I first learned about my RCC diagnosis, I was curious about the various treatment options available, including surgery. In this section, we will discuss the role of surgery in treating advanced RCC and the different types of surgical procedures that may be recommended. In some cases, removing the entire affected kidney (known as a nephrectomy) may be the best course of action, while in other situations, a partial nephrectomy (removal of only the tumor and a small margin of healthy tissue) may suffice.
Additionally, lymph node dissection may be performed to determine if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. It's important to remember that the decision to undergo surgery depends on various factors, such as the stage of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and the potential risks and benefits of the procedure. Be sure to discuss these factors with your healthcare team to determine if surgery is the right choice for you.
Exploring Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapy
Aside from surgery, there are other treatment options for advanced RCC, including targeted therapies and immunotherapy. Targeted therapies are drugs that specifically target the cancer cells, helping to block their growth and spread. Some examples of targeted therapies used to treat advanced RCC include tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as sunitinib and pazopanib, and mTOR inhibitors, like temsirolimus and everolimus.
Immunotherapy, on the other hand, is a type of treatment that utilizes the body's immune system to fight cancer. Some examples of immunotherapy drugs used to treat advanced RCC are nivolumab and ipilimumab. It's important to note that these treatments may cause side effects, so be sure to discuss the potential risks and benefits with your healthcare team before starting any new treatment regimen.
Understanding the Role of Radiation and Chemotherapy
During my journey with RCC, I learned that radiation therapy and chemotherapy play a different role in treating this type of cancer compared to other cancers. In this section, we'll explore why these treatments may not be as effective for RCC and when they might be considered as an option. Unlike other cancers, RCC tends to be resistant to conventional chemotherapy. However, in some cases, chemotherapy may still be used if other treatments have not been effective.
Radiation therapy is typically not used as a primary treatment for RCC, but it may be recommended in certain circumstances, such as to alleviate pain or prevent complications caused by metastases. Keep in mind that the decision to pursue these treatments should be made in consultation with your healthcare team, taking into account the potential risks and benefits.
Managing Side Effects and Improving Quality of Life
Dealing with the side effects of advanced RCC and its treatments can be challenging. In this section, we'll discuss some strategies to help manage these side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and pain, and improve your overall quality of life. It's essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized plan to address your specific needs, which may include medications, physical therapy, or complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or massage.
Furthermore, don't underestimate the power of emotional support. Reach out to your friends, family, or support groups to help you navigate the ups and downs of living with advanced RCC. Remember, you don't have to face this journey alone.
Preparing for the Future: Advanced Care Planning
As someone living with advanced RCC, it's important to think about the future and make plans for your care as the disease progresses. In this section, we'll discuss the importance of advanced care planning and how to approach this difficult but necessary process. This may involve discussing your wishes with your healthcare team and loved ones, setting up a living will, and appointing a healthcare proxy who can make medical decisions on your behalf if you're unable to do so.
Addressing these matters ahead of time can help ensure that your preferences are respected and give you and your family peace of mind. Remember, advanced care planning is an ongoing process, so be sure to revisit these plans as your situation changes or if new treatment options become available.


Bart Cheever
The article is okay.
May 12, 2023 AT 22:27
Shouvik Mukherjee
I appreciate how the post breaks down each treatment option in clear steps. It can be reassuring for anyone feeling overwhelmed by the medical jargon. Keep sharing such thorough resources.
May 30, 2023 AT 09:11
Ben Hooper
The staging information is presented in a logical order. Each stage description links directly to treatment considerations. Readers can follow the progression without feeling lost. The layout aids quick reference.
June 16, 2023 AT 19:54
Melissa H.
Your personal narrative brings a human face to a complex disease. I admire the courage you display while outlining each therapeutic avenue. The way you detail symptom awareness empowers patients to seek help sooner. Highlighting fatigue, hematuria, and back pain underscores the subtlety of early signs. You correctly note that these symptoms overlap with benign conditions, which can delay diagnosis. Your explanation of the TNM staging system demystifies a topic that often intimidates newcomers. By separating T, N, and M components you make the hierarchy easier to grasp. The discussion of surgical options, from radical nephrectomy to partial procedures, offers a balanced view of risks and benefits. I especially value the inclusion of lymph node dissection as a diagnostic tool. The overview of targeted therapies such as TKIs and mTOR inhibitors reflects current standards of care. Your brief on immunotherapy agents like nivolumab and ipilimumab shows awareness of emerging treatments. Addressing side effect management demonstrates a holistic approach to patient wellbeing. The suggestion to incorporate complementary modalities like acupuncture adds depth to the care plan. You rightly emphasize emotional support networks, reminding us that cancer is fought on many fronts. The section on advanced care planning is handled with sensitivity and practicality. Overall, your comprehensive guide serves as both an educational tool and a source of motivation for those navigating advanced RCC :)
July 4, 2023 AT 06:38
Edmond Abdou
This post does a great job of covering both medical facts and the emotional journey. It’s refreshing to see practical advice alongside encouragement. Thank you for sharing such a well‑rounded guide 😊
July 21, 2023 AT 17:22
Sydnie Baker
The exposition exhibits a commendable synthesis of oncologic nomenclature and patient‑centric discourse. By interlacing pathophysiological lexicon with lay‑accessible analogies, the author cultivates a veritable nexus of erudition and empathy. The articulation of cytoreductive nephrectomy, juxtaposed with immunomodulatory regimens, reflects an astute appreciation of contemporary therapeutic paradigms. Moreover, the deliberation on palliative radiotherapy underscores a nuanced appreciation of symptom palliation versus curative intent.
August 8, 2023 AT 04:06
Benjie Gillam
I think ur point about the balance between jargon and clarity is spot on. It can be tricky to keep teh language both accurate and understandable. Your take adds depth to the discussion.
August 25, 2023 AT 14:50
Eric Parsons
The article successfully integrates clinical detail with compassionate guidance. Its structured approach facilitates quick reference for both patients and caregivers. Maintaining this level of clarity can greatly improve health literacy. Kudos to the author for the thorough presentation.
September 12, 2023 AT 01:33